Question #577df
1 Answer
Radioactivity is the process by which the (unstable) nucleus of an atom disintegrates (i.e. breaks down to form different particles/ releases energy).
Explanation:
In short, if a nucleus of an atom decays spontaneously, it is deemed radioactive. For instance, unstable thorium or carbon-14 nuclei often decay and are, therefore, radioactive. There are three common forms of such radioactive decay:
- Alpha decay: an alpha particle is released
- Beta decay: an electron or positron (positive electron)
- Gamma decay: a photon/high energy particle is released
For example (alpha-decay):
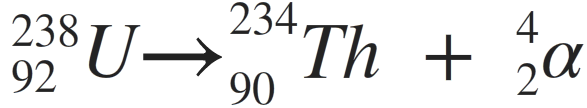
In all cases, radioactivity is present as:
- An unstable nucleus has decayed (in the example above, the uranium nucleus decays into thorium)
- A particle (in the example above, a helium nucleus/alpha particle) or energy (gamma) has been released