How do I determine the molecular shape of a molecule?
1 Answer
WARNING. This is a LONG document. It covers all possible shapes for molecules with up to six electron pairs around the central atom.
Explanation:
STEPS INVOLVED
There are three basic steps to determining the molecular shape of a molecule:
-
Write the Lewis dot structure of the molecule. That gives you the steric number (SN) — the number of bond pairs and lone pairs around the central atom.
-
Use the SN and VSEPR theory to determine the electron pair geometry of the molecule.
-
Use the VSEPR shape to determine the angles between the bonding pairs.
VSEPR PRINCIPLES:
-
The repulsion between valence electron pairs in the outer shell of the central atom determines the shape of the molecule. You must determine the steric number (SN) — the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs about the central atom.
-
Lone pairs repel more than bond bonding pairs.
A. SN = 2
What is the shape of
The Lewis dot structure for

The central
Repulsion between these two pairs causes the atoms to be as far apart as possible.
The shape of the molecule is linear, and the
B. SN = 3
There are two possibilities.
i.
What is the shape of
The Lewis dot structure
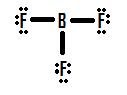
The
Minimizing the repulsion causes the

The shape of the molecule is trigonal planar.
All the atoms are in the same plane, and the
ii.
What is the shape of
The Lewis dot structure

The central atom,
The electron pair geometry of
It would be drawn as

The molecular shape of
In determining the molecular shape, we consider only the positions of the atoms, not the lone pairs.
Hence, the molecular shape of

The lone pair of electrons occupies a relatively large volume, since they are held by only one atom.
They compress the bond angle between the oxygens and sulfur to about 119.5°.
C. SN = 4
There are four possibilities.
i.
What is the shape of
The Lewis dot structure

The shape of this molecule, however, is not planar, as you might think from the way we draw this dot structure.
The four bond pairs are arranged about the
This shape minimizes the repulsion between the bond pairs.

The 109.5° angle is the same for all
The shape of the
ii.
What is the molecular geometry of
The Lewis dot structure of

The central atom,
The electron pair geometry of
It is drawn as shown below:

Remember that, in determining the molecular shape, we consider only the positions of the atoms, not the lone pairs.
If we look only at the atoms, we see a short, rather distorted tetrahedron.
This is called a pyramid.
The
Hence the shape is trigonal pyramidal.
The greater repulsion of the lone pair causes the
In
iii.
What is the molecular geometry of
The Lewis dot structure of

The central atom,
The electron pair geometry of
It is drawn as shown below:

The shape is called bent.
The
In water, the observed
All bond angles in
D. SN = 5
There are four possibilities.
i.
What is the molecular shape of
The Lewis dot structure of
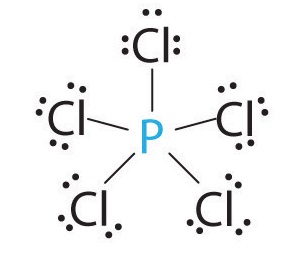
Atoms past
Here, the
If you view the

Note that the
The two
The other three
If you join the
The
There are two different bond angles in the molecule.
The axial
ii.
What is the molecular shape of
The Lewis dot structure of
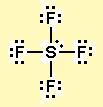
The five electron pairs assume a trigonal bipyramidal geometry.

The lone pair occupies an equatorial position, because that gets it furthest away from the other electron pairs.
If you turn the molecule on its side, it looks like a see-saw, with the axial
The shape is called a see-saw.

The axial
The equatorial
iii.
What is the molecular shape of
The Lewis dot structure of
https://s3.amazonaws.com/classconnection/153/flashcards/919153/png/download_(3)-1518046CE7937FB18BB.png
The five electron pairs assume a trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
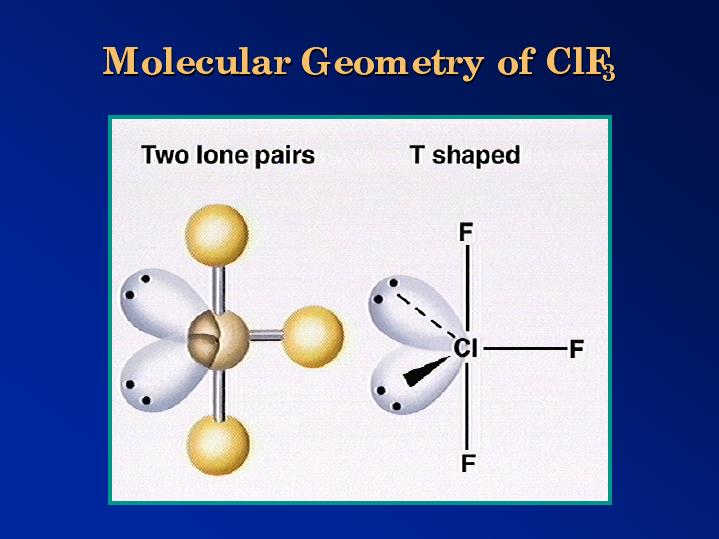
The two lone pairs occupy the equatorial positions in order to minimize repulsions.
The bonding pairs form a T-shape, and that is the shape of the molecule.

Actually, the molecule has a “distorted-T” shape because the two lone pairs reduce the
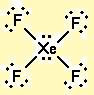
iv.
What is the molecular shape of
The Lewis dot structure of

The five electron pairs assume a trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
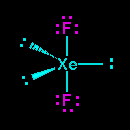
The three lone pairs occupy the three equatorial positions, so what you have is a xenon atom with three lone pairs pointing toward the corners of an equilateral triangle, with one
The result is a linear shape for the
E. SN = 6
There are five possibilities.
i.
What is the molecular shape of
The Lewis dot structure of

The six bonding pairs arrange themselves with four equatorial bond pairs and one more pair at each of the polar locations.

The shape is called octahedral.
Every
ii.
What is the structure of
The Lewis dot structure of
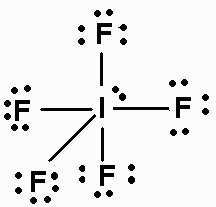
The electron pairs arrange themselves at the corners of an octahedron with a lone pair occupying one of these positions.
Four of the
Lines connecting the
The
iii.
What is the molecular shape of
The Lewis dot structure is
The electron pairs arrange themselves at the corners of an octahedron.
The four bonding pairs point toward the corners of a square, and the lone pairs occupy the axial positions above and below the plane of the square.

Since the four
The
iv.
There are no molecules that belong to the
However, the electron geometry is octahedral, with the three lone pairs occupying equatorial positions.
The remaining bond pairs are arranged in a T-shape with bond angles of 90°.
![]()
v.
No stable
However, we predict the molecular shape to be linear with bond angles of 180°.
![]()
SUMMARY
To predict the shape of a molecule:
-
Write the Lewis dot structure for the molecule.
-
Determine the steric number of the central atom.
-
Decide on the electron pair orientation based on the steric number.
-
Consider the placement of lone pairs and any distortions from "regular" shapes.
-
Name the shape based on the location of atoms attached to the central atom
The table below summarizes all the molecular shapes.



