How do intermolecular forces affect evaporation?
1 Answer
The larger the intermolecular forces in a compound, the slower its evaporation rate.
In order of decreasing strength, the important intermolecular forces in a compound are
• Hydrogen Bonds
• Dipole-dipole attractions
• London dispersion forces
They all depend on the fact that some parts of polar molecules have positive charges and other parts have negative charges. The positively charged parts on one molecule align with the negative parts of other molecules.
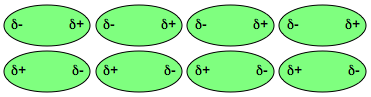
These forces of attraction hold polar liquids together.

If the molecules are held tightly together by strong intermolecular forces, few of the molecules will have enough kinetic energy to separate from each other.
They will stay in the liquid phase, and the rate of evaporation will be low.
If the molecules are held loosely together by van der Waals forces, many of them will have enough kinetic energy to separate from each other.
They will escape from the liquid phase, and the rate of evaporation will be high.


