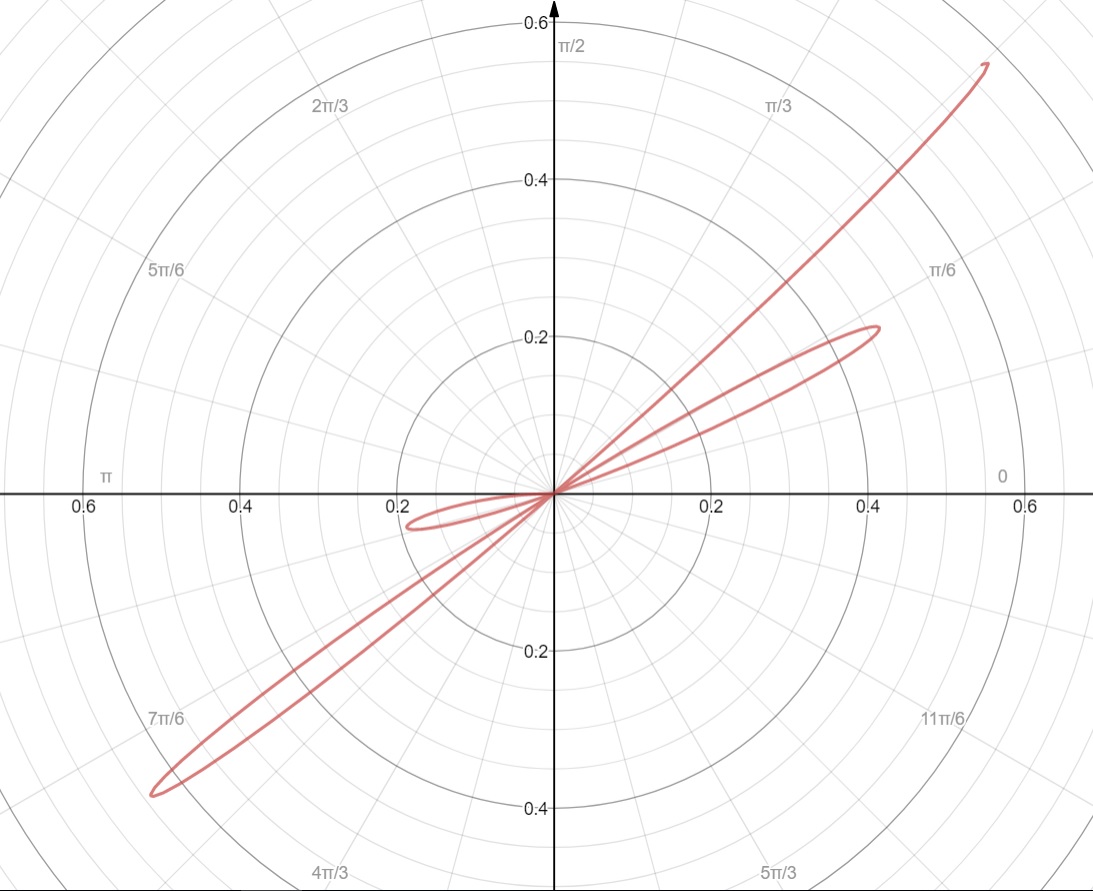
To determine an area in polar coordinates, it first helps to look at the graph that is depicted by the given parameters:
#r=-thetasin(-16theta^2+(7pi)/12)# with #theta in [0, pi/4]#
 )
)
Not every bit of the graph in within #[0,pi/4]# is an enclosed area or loop. Once we find the #r# and #theta# values corresponding to the three loops, we can use them as limits of integration. Each area formed by a loop can be determined by the formula:
#A=int_a^b1/2f[theta]^2 d theta#
Three loops, means three integrals. The roots of radius, #r#, will give us the limits of integration.
#-thetasin(-16theta^2+(7pi)/12) = 0#
The trivial solution is when #theta=0#. Because the sine function is zero at #pi n#, we can say #sin(-16 theta^2 +(7pi)/12)=0# whenever
#-16 theta^2 + (7pi)/12 = pi n#
#-16 theta^2 = pi n - (7pi)/12#
#theta^2 = -(pi n)/16 + (7 pi)/192#
#theta = +-sqrt(-(pi n)/16 + (7 pi)/192)#
We know #theta# is restricted to the interval #[0, pi//4]#. Because our interval involves only positive values, then we can write:
#0 <= sqrt(-(pi n)/16 + (7 pi)/192) <= pi/4#
#0 <= -(pi n)/16 + (7 pi)/192 <= pi^2/16#
#0 <= -pi n + (7 pi)/12 <= pi^2#
#-(7 pi)/12 <= -pi n <= pi^2 - (7 pi)/12#
#7/12 >= n >= -pi + 7/12#
#-2.55826 <= n <= 0.583333#
The integers, #n#, that lie on this interval are #-2, -1, 0#. The respective angles, #theta#, with those values of #n# are #theta=0# and:
#theta ~~0.3384, 0.5576, 0.7122#
Now we have our limits of integration for three integrals.
#A_1=int_0^0.3384 1/2[-thetasin(-16theta^2+(7pi)/12)]^2 d theta#
#A_2=int_0.3384^0.5576 1/2[-thetasin(-16theta^2+(7pi)/12)]^2 d theta#
#A_3=int_0.5576^0.7122 1/2[-thetasin(-16theta^2+(7pi)/12)]^2 d theta#
Using a computer algebra system, we get
#A_1 = 0.0057972#
#A_2 = 0.0225589#
#A_3 = 0.0313656#
#A_"Total" = 0.0597217#
 )
) 