How do you evaluate the integral of #x^2# from 1 to 2?
1 Answer
Feb 18, 2016
Explanation:
Here, we have
If
#int_a^bf(x)dx=F(b)-F(a)#
So, when we have
#int_1^2x^2dx#
we must find the antiderivative of the function
#intx^ndx=x^(n+1)/(n+1)+C#
Using this rule, we see that
Thus,
#int_1^2x^2dx=F(2)-F(1)#
Note that
#F(2)-F(1)=2^3/3-1^3/3=8/3-1/3=7/3#
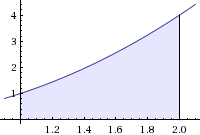
This means that the area between the

