What is the molecular orbital diagram for #B_2#?
1 Answer
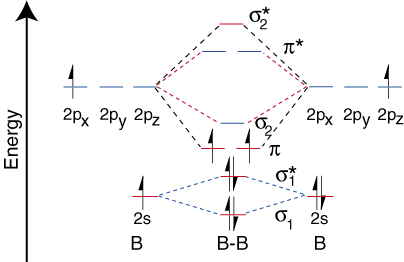
Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals.
Then we rank them in order of increasing energy.
We can ignore the
Each boron atom has one
The
The
The
The order of energies is
We have three valence electrons from each B atom, so B₂ will have six valence electrons.
We use the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's rule to fill the orbitals in an Aufbau process.
The molecular orbital diagram for B₂ then becomes
The video below describes how to generate molecular orbital diagrams for B₂ and other diatomic molecules from Row 2 elements of the Periodic Table.

