How do you solve #tan(x+pi)+2sin(x+pi)=0#?
1 Answer
For this type of problem, you must use the double angle formulae to expand the parentheses.
Explanation:
The following formulas are extremely important. Be sure to retain them into the future.
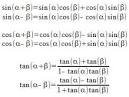
Now, using these formulae, we can expand:
Note that these solutions are only in the interval
Hopefully this helps!

